Human-wildlife conflict is a major obstacle to conservation and development globally, occurring when wildlife and human needs for resources overlap, leading to competition.
Factors aggravating HWC include increases in human, livestock, and wildlife populations, agricultural expansion, deforestation, illegal activities in protected areas, climate change, and encroachment into wildlife corridors.
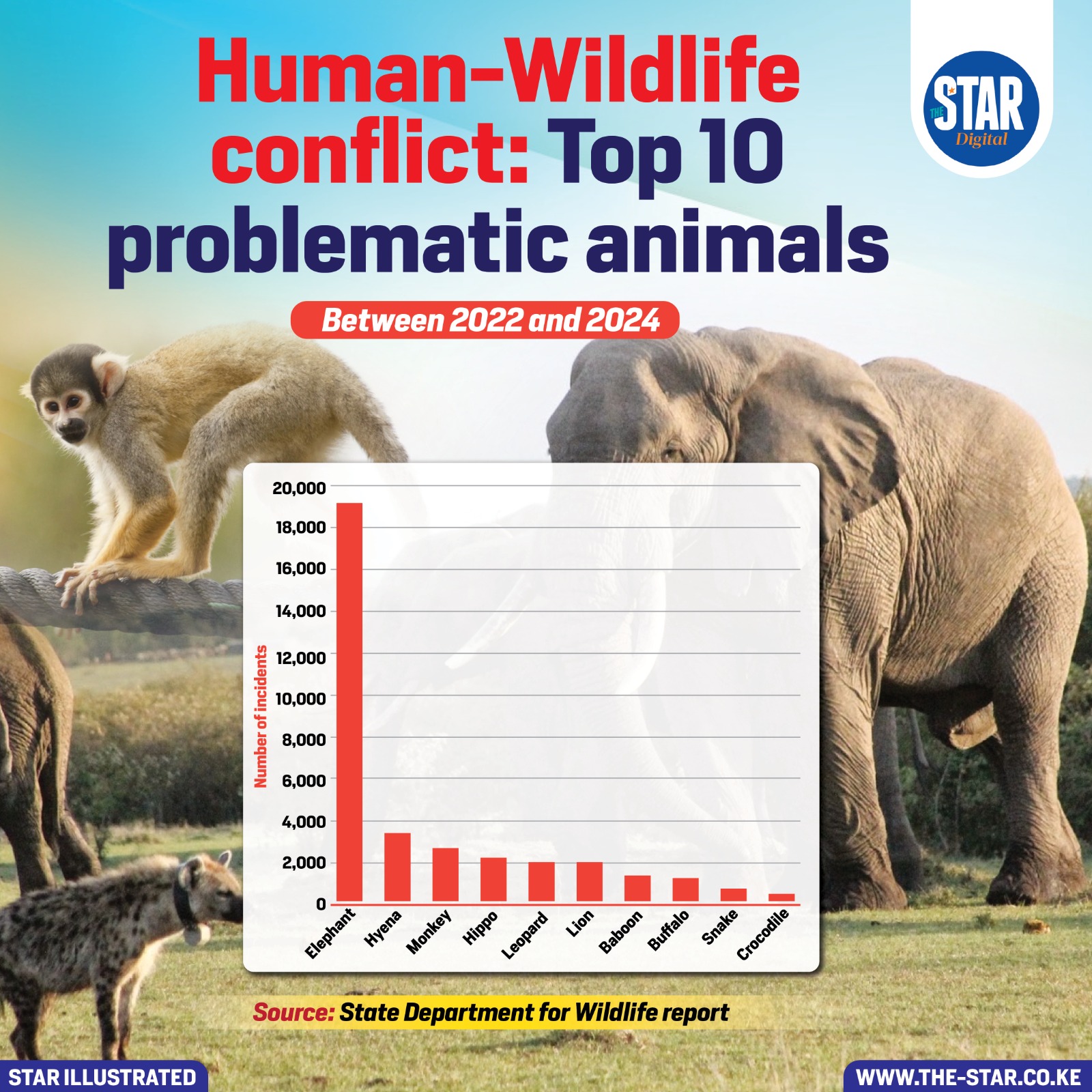
For the period between 2022 and 2024, the top ten species involved in human-wildlife conflicts were Elephants, contributing to the highest number of incidents during this specific period.

















