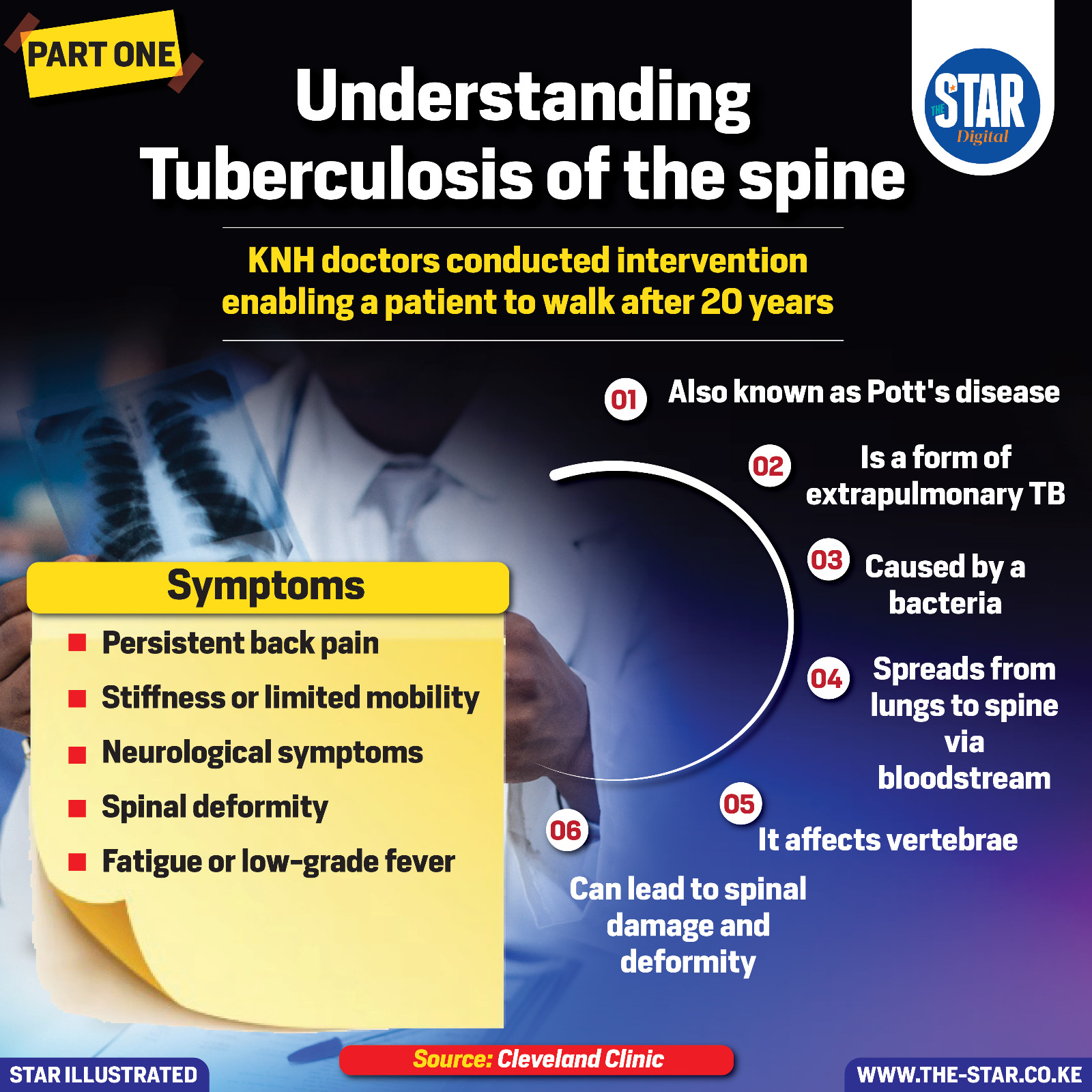
Tuberculosis of the spine, also known as Pott’s disease, is a form of extrapulmonary TB caused by a bacteria that spreads from the lungs to the spine through the bloodstream.
It affects the vertebrae and can lead to spinal damage and deformity.
Symptoms include persistent back pain, stiffness or limited mobility, neurological symptoms, spinal deformity, and fatigue or low-grade fever.
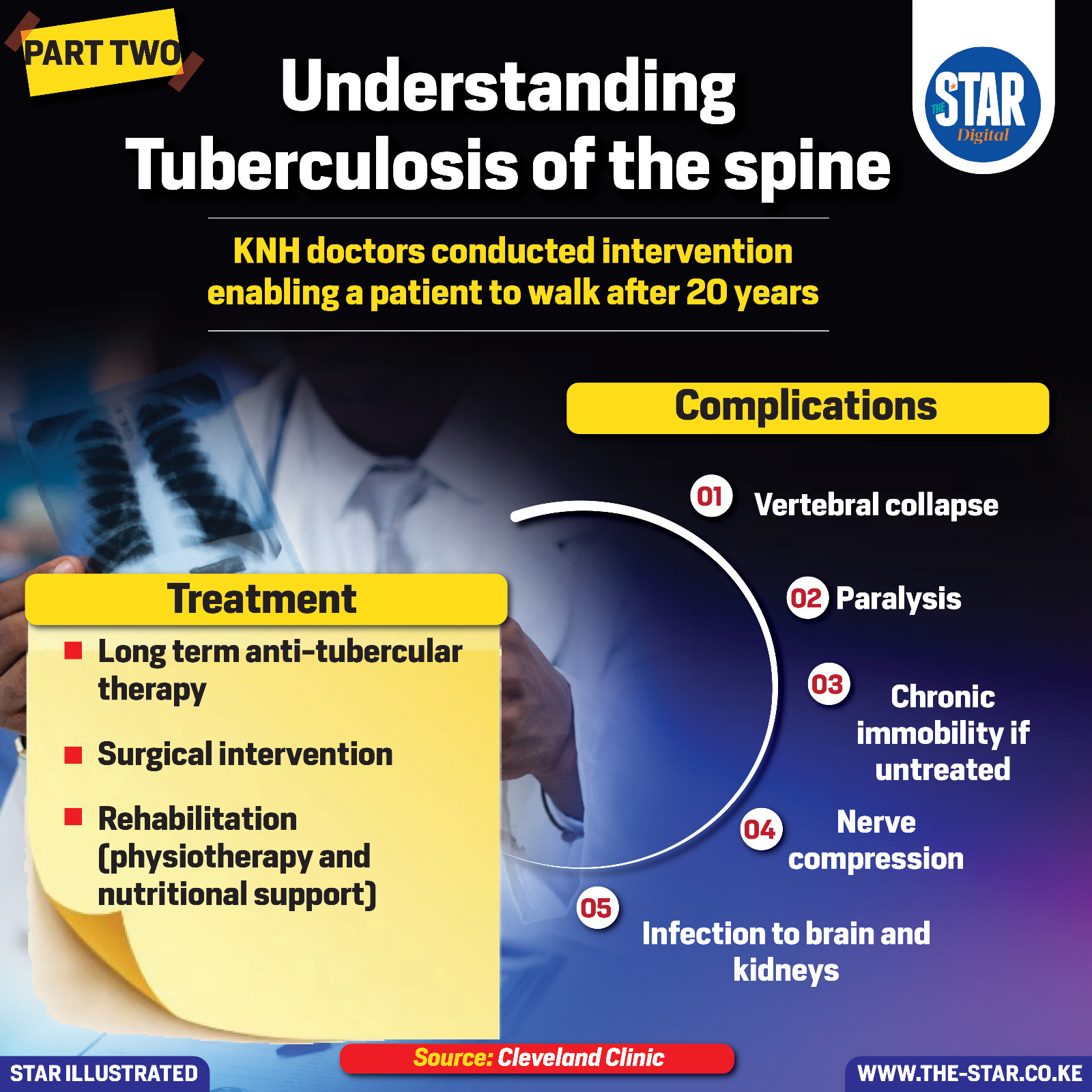
Complications may involve vertebral collapse, paralysis, chronic immobility if untreated, nerve compression, and infection to the brain and kidneys.
Treatment requires long-term anti-tubercular therapy, surgical intervention, and rehabilitation through physiotherapy and nutritional support.